虚幻默认带有好几种不同的Allocator实现,用来实现不同的malloc/free策略。有一些调试用的Allocator可以用来查内存相关的bug。
Windows下的Allocator选择
编辑器下,UE4默认使用TBB Allocator,TBB不可用的情况下到Mimalloc (UE5默认Mimalloc)。非shipping情况下,可以靠传参设置allocator
-ansimalloc,绕开所有的allocator,用操作系统原生的new/delete,方便valgrind等工具-tbbmalloc,使用TBB Allocator- 打包版本默认使用
Binned2/Binned3Allocator
调试用allocator
-stompmalloc分配虚拟内存的时候不会复用已有的地址,分配内存的时候会分配一个额外的保护页,越界写会立刻崩溃-stompmalloc2ue5 only,没看实现PoisonMallocProxy在UE打包的时候的Development版本会有,内存回收以后会设置成一个特殊的值,防止野指针
简化版的选择逻辑如下
FMalloc* FWindowsPlatformMemory::BaseAllocator()
{
if (FORCE_ANSI_ALLOCATOR) //-V517
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Ansi;
}
// UE4 编辑器情况下默认会进这个分支,用TBB Allocator
else if ((WITH_EDITORONLY_DATA || IS_PROGRAM) && TBB_ALLOCATOR_ALLOWED) //-V517
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::TBB;
}
#if PLATFORM_64BITS
else if ((WITH_EDITORONLY_DATA || IS_PROGRAM) && MIMALLOC_ALLOCATOR_ALLOWED) //-V517
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Mimalloc;
}
else if (USE_MALLOC_BINNED3)
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned3;
}
#endif
else if (USE_MALLOC_BINNED2)
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned2;
}
else
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned;
}
#if !UE_BUILD_SHIPPING
// If not shipping, allow overriding with command line options, this happens very early so we need to use windows functions
const TCHAR* CommandLine = ::GetCommandLineW();
if (FCString::Stristr(CommandLine, TEXT("-ansimalloc")))
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Ansi;
}
#if TBB_ALLOCATOR_ALLOWED
else if (FCString::Stristr(CommandLine, TEXT("-tbbmalloc")))
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::TBB;
}
#endif
#if MIMALLOC_ALLOCATOR_ALLOWED
else if (FCString::Stristr(CommandLine, TEXT("-mimalloc")))
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Mimalloc;
}
#endif
#if PLATFORM_64BITS
else if (FCString::Stristr(CommandLine, TEXT("-binnedmalloc3")))
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned3;
}
#endif
else if (FCString::Stristr(CommandLine, TEXT("-binnedmalloc2")))
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned2;
}
else if (FCString::Stristr(CommandLine, TEXT("-binnedmalloc")))
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned;
}
#if WITH_MALLOC_STOMP
else if (FCString::Stristr(CommandLine, TEXT("-stompmalloc")))
{
AllocatorToUse = EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Stomp;
}
#endif // WITH_MALLOC_STOMP
#endif // !UE_BUILD_SHIPPING
switch (AllocatorToUse)
{
case EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Ansi:
return new FMallocAnsi();
#if WITH_MALLOC_STOMP
case EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Stomp:
return new FMallocStomp();
#endif
#if TBB_ALLOCATOR_ALLOWED
case EMemoryAllocatorToUse::TBB:
return new FMallocTBB();
#endif
#if MIMALLOC_ALLOCATOR_ALLOWED && PLATFORM_SUPPORTS_MIMALLOC
case EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Mimalloc:
return new FMallocMimalloc();
#endif
case EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned2:
return new FMallocBinned2();
#if PLATFORM_64BITS
case EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned3:
return new FMallocBinned3();
#endif
default: // intentional fall-through
case EMemoryAllocatorToUse::Binned:
return new FMallocBinned((uint32)(GetConstants().BinnedPageSize&MAX_uint32), (uint64)MAX_uint32 + 1);
}
}
StompMalloc的实现
StompMalloc实现的挺好的,主要是在分配的时候会分配一个额外的保护页,越界写会立刻崩溃。
主要看 Malloc和Free的实现。图片来自Pablo Zurita
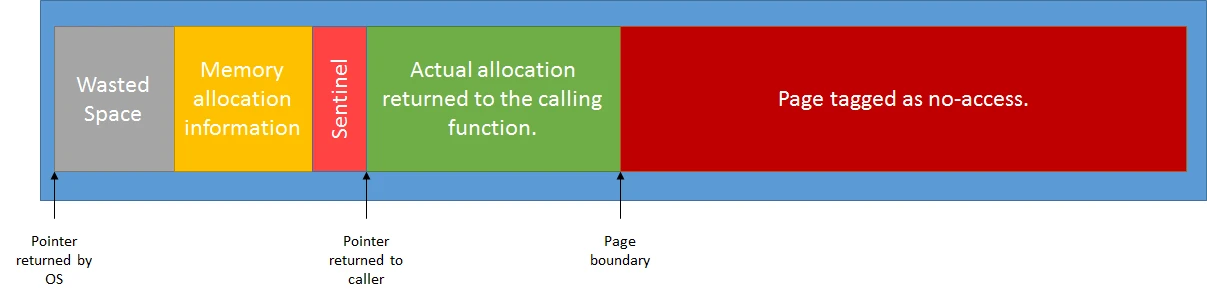
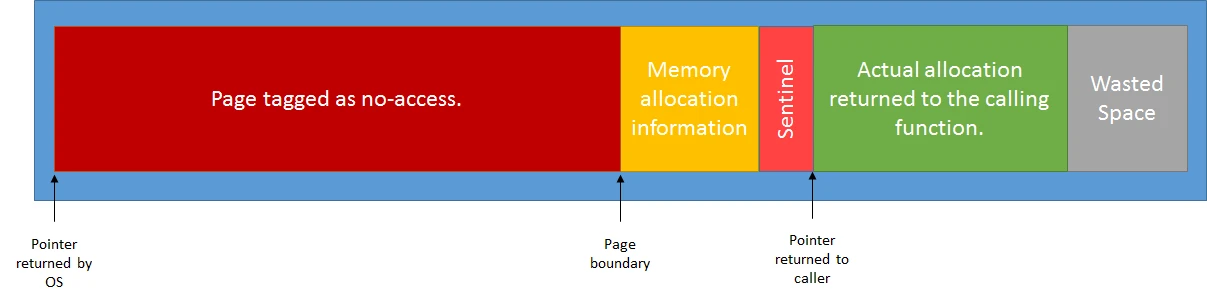
内存踩踏有三种:
- 正向越界写
- 负向越界写(比如倒序遍历没有终止,写了arr[-1]这种)
- 释放后读/写
- StompMalloc对于前两种情况,在分配时候会额外分配一个页,并且设置保护,这样越界写的时候就会触发崩溃。区别是保护页在头部还是尾部。
- 在释放的时候,StompAllocator会归还物理内存,但是不会释放虚拟地址,这样对虚拟地址的读写(use-after-free)会报错。
虚幻默认检查正向越界写,对负向越界写的检查需要自己改一下StompAllocator创建的部分,构造函数需要传个参数过去。
Malloc
struct FAllocationData
{
/** Pointer to the full allocation. Needed so the OS knows what to free. */
void *FullAllocationPointer;
/** Full size of the allocation including the extra page. */
SIZE_T FullSize;
/** Size of the allocation requested. */
SIZE_T Size;
/** Sentinel used to check for underrun. */
SIZE_T Sentinel;
};
void* FMallocStomp::TryMalloc(SIZE_T Size, uint32 Alignment)
{
if (Size == 0U)
{
Size = 1U;
}
#if PLATFORM_64BITS
// 64-bit ABIs on x86_64 expect a 16-byte alignment
Alignment = FMath::Max<uint32>(Alignment, STOMPALIGNMENT);
#endif
const SIZE_T AlignedSize = (Alignment > 0U) ? ((Size + Alignment - 1U) & -static_cast<int32>(Alignment)) : Size;
const SIZE_T AllocFullPageSize = AlignedSize + sizeof(FAllocationData) + (PageSize - 1) & ~(PageSize - 1U); // 一个简单的公式,对着PageSize向上取整
const SIZE_T TotalAllocationSize = AllocFullPageSize + PageSize; // 还会额外分配一个PageSize, windows 64bit典型值是 4 kb
// 走mmap / virtualalloc分配,直接调用系统的API,不走C库的malloc了
// 因为这里本来就是在实现malloc...
// MAP_ANONYMOUS 标记表示这里在分配内存,没有任何file, fd 应该传入-1
#if PLATFORM_UNIX || PLATFORM_MAC
void *FullAllocationPointer = mmap(nullptr, TotalAllocationSize, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANON, /*fd*/-1, /*offset*/0);
#elif PLATFORM_WINDOWS && MALLOC_STOMP_KEEP_VIRTUAL_MEMORY
// Allocate virtual address space from current block using linear allocation strategy.
// If there is not enough space, try to allocate new block from OS. Report OOM if block allocation fails.
void* FullAllocationPointer = nullptr;
if (VirtualAddressCursor + TotalAllocationSize <= VirtualAddressMax)
{
FullAllocationPointer = (void*)(VirtualAddressCursor);
}
else
{
const SIZE_T ReserveSize = FMath::Max(VirtualAddressBlockSize, TotalAllocationSize);
// Reserve a new block of virtual address space that will be linearly sub-allocated
// We intentionally don't keep track of reserved blocks, as we never need to explicitly release them.
FullAllocationPointer = VirtualAlloc(nullptr, ReserveSize, MEM_RESERVE, PAGE_NOACCESS);
VirtualAddressCursor = UPTRINT(FullAllocationPointer);
VirtualAddressMax = VirtualAddressCursor + ReserveSize;
}
// No atomics or locks required here, as Malloc is externally synchronized (as indicated by FMallocStomp::IsInternallyThreadSafe()).
VirtualAddressCursor += TotalAllocationSize;
#else
// 其他系统不支持的话,回落到bin allocator
void *FullAllocationPointer = FPlatformMemory::BinnedAllocFromOS(TotalAllocationSize);
#endif // PLATFORM_UNIX || PLATFORM_MAC
if (!FullAllocationPointer)
{
return nullptr;
}
void* ReturnedPointer = nullptr;
static const SIZE_T AllocationDataSize = sizeof(FAllocationData);
// 初始化一个AllocData结构体作为header
const FAllocationData AllocData = { FullAllocationPointer, TotalAllocationSize, AlignedSize, SentinelExpectedValue };
// 这里要区分Overrun和Underrun,两者的header摆放有点不同..看Overrun的
if(bUseUnderrunMode)
{
// 保护页 | header | 内容
// header必须在前面的原因是因为只有拿到header才能正常free..不然没办法知道这个块分配了多少
// 所以underrun的情况会更难检查一点,因为要underrun了AllocationData的大小(32字节)才会到保护页
// 不过如果把header的哨兵值写坏了,free的时候可以发现
const SIZE_T AlignedAllocationData = (Alignment > 0U) ? ((AllocationDataSize + Alignment - 1U) & -static_cast<int32>(Alignment)) : AllocationDataSize;
ReturnedPointer = reinterpret_cast<void*>(reinterpret_cast<uint8*>(FullAllocationPointer) + PageSize + AlignedAllocationData);
void* AllocDataPointerStart = reinterpret_cast<FAllocationData*>(reinterpret_cast<uint8*>(FullAllocationPointer) + PageSize);
// 保护第一页
#if PLATFORM_WINDOWS && MALLOC_STOMP_KEEP_VIRTUAL_MEMORY
// Commit physical pages to the used range, leaving the first page unmapped.
void* CommittedMemory = VirtualAlloc(AllocDataPointerStart, AllocFullPageSize, MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_READWRITE);
if (!CommittedMemory)
{
// Failed to allocate and commit physical memory pages.
return nullptr;
}
check(CommittedMemory == AllocDataPointerStart);
#else
// Page protect the first page, this will cause the exception in case the is an underrun.
FPlatformMemory::PageProtect(FullAllocationPointer, PageSize, false, false);
#endif
} //-V773
else
{
// 检查overrun的情况,需要把分配的结果的尾部紧贴着保护页,保护页在后面
// Header | 内容 | 保护页
ReturnedPointer = reinterpret_cast<void*>(reinterpret_cast<uint8*>(FullAllocationPointer) + AllocFullPageSize - AlignedSize);
#if PLATFORM_WINDOWS && MALLOC_STOMP_KEEP_VIRTUAL_MEMORY
// windows的话,留着最后一个页的属性为PAGE_NOACCESS
// Commit physical pages to the used range, leaving the last page unmapped.
void* CommittedMemory = VirtualAlloc(FullAllocationPointer, AllocFullPageSize, MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_READWRITE);
if (!CommittedMemory)
{
// Failed to allocate and commit physical memory pages
return nullptr;
}
check(CommittedMemory == FullAllocationPointer);
#else
// FUnixPlatformMemory::PageProtect(void* const Ptr, const SIZE_T Size, const bool bCanRead, const bool bCanWrite)
// *nix的话,调用mprotect, 把最后一页的属性设置为PROT_NONE
// https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/mprotect.2.html
// Page protect the last page, this will cause the exception in case the is an overrun.
FPlatformMemory::PageProtect(reinterpret_cast<void*>(reinterpret_cast<uint8*>(FullAllocationPointer) + AllocFullPageSize), PageSize, false, false);
#endif
} //-V773
// 在return pointer前面加入header 头
FAllocationData* AllocDataPointer = reinterpret_cast<FAllocationData*>(reinterpret_cast<uint8*>(ReturnedPointer) - AllocationDataSize);
*AllocDataPointer = AllocData;
return ReturnedPointer;
}
Free
Free主要都是利用系统API提供的能力。 可以把物理内存归还给系统,但是虚拟地址不释放,这样虚拟地址会进入Reserved状态(Windows)。任何读写都会直接抛异常。 Linux写的比较模糊,只是描述了一下munmap以后,对释放的虚拟地址读写都会触发错误。
void FMallocStomp::Free(void* InPtr)
{
if(InPtr == nullptr)
{
return;
}
//Header一定在前面,所以这里减去FAllocationData的偏移量就是header的地址
FAllocationData *AllocDataPtr = reinterpret_cast<FAllocationData*>(InPtr);
AllocDataPtr--;
// Check that our sentinel is intact.
if(AllocDataPtr->Sentinel != SentinelExpectedValue)
{
// There was a memory underrun related to this allocation.
UE_DEBUG_BREAK();
}
#if PLATFORM_UNIX || PLATFORM_MAC
// The munmap() system call deletes the mappings for the specified
// address range, and causes further references to addresses within
// the range to generate invalid memory references.
munmap(AllocDataPtr->FullAllocationPointer, AllocDataPtr->FullSize);
#elif PLATFORM_WINDOWS && MALLOC_STOMP_KEEP_VIRTUAL_MEMORY
// Unmap physical memory, but keep virtual address range reserved to catch use-after-free errors.
#if USING_CODE_ANALYSIS
MSVC_PRAGMA(warning(push))
MSVC_PRAGMA(warning(disable : 6250)) // Suppress C6250, as virtual address space is "leaked" by design.
#endif
// https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/memoryapi/nf-memoryapi-virtualfree
// If a page is decommitted but not released, its state changes to reserved. Subsequently, you can call VirtualAlloc to commit it, or VirtualFree to release it.
// Attempts to read from or write to a reserved page results in an access violation exception.
VirtualFree(AllocDataPtr->FullAllocationPointer, AllocDataPtr->FullSize, MEM_DECOMMIT);
#if USING_CODE_ANALYSIS
MSVC_PRAGMA(warning(pop))
#endif
#else
FPlatformMemory::BinnedFreeToOS(AllocDataPtr->FullAllocationPointer, AllocDataPtr->FullSize);
#endif // PLATFORM_UNIX || PLATFORM_MAC
}